A laboratory beaker is a beverage container and a term used in parts of the United Kingdom. Usually a laboratory beaker is a non-disposable plastic or ceramic cup or cup without a handle, such as a laboratory beaker.
The laboratory beaker is particularly used to describe a cup with a lid designed for toddlers or small children, with a non-spill spout built into the lid. In North American English, the term is used almost exclusively in the context of the laboratory. Glasses of a similar shape in North America are known as drums.
🌡 How long does a laboratory beaker hold up?
Standard or low-shaped glasses are usually about 1.4 times the diameter in height. The common low shape with a spout was designed by John Joseph Griffin, and therefore it is sometimes called Griffin's glass.
These are the most universal characters and are used for various purposes, from the preparation of solutions and the decantation of supernatant liquids to the retention of waste liquids before their disposal to the conduct of simple reactions.
In short, it is likely that low-form vessels will be used in some way when conducting almost any chemical experiment. Tall-shaped beakers (B) have a height of about twice their diameter.
These are sometimes called Berzelius vessels and are mainly used for titration. The flat beakers (C) are normally called crystallizers because they are generally used to make the crystallization, but they are also used as a container to be used in a hot bath. These vessels usually do not have a flat scale.
A beaker is distinguished from a flask by having straight rather than sloping sides. The uniqueness to this explanation is a subtly conical beaker named Philips beaker.
👉 What is a beaker for
It is a tubular container that is used to store, combine and heat solutions in a laboratory. They are generally made of glass, but in turn other types of non-destructive materials are used, such as plastic and metal that withstand heat.
Glasses usually have flat bottoms and a rim around the top. Its dimension changes from one millimeter to several liters. Bunsen lighters, heating plates, stirrers, safety tongs, safety glasses, gloves and lab coats are utensils that are usually used when working with containers.
Pour the liquid into the beaker, add slowly to avoid splashing the liquid. Use the measuring margins on the laboratory beaker to approximate the volume of the fluid in the beaker. Stir the liquid inside the glass with a spoon or shaker.
Place the beaker in a Bunsen flame to heat the fluid, if required; do not fill the container more than 1/3 full during heating and always use tongs as safety when handling a hot glass. Pour the liquid from the beaker using the spout on the rim around the top of the glass.


🔹 Beaker precautions
* Place the Bunsen burner well away from the edge of the bench.
* Do not fill the container more than halfway.
• If available, add an anti-shock granule to the liquid before heating. Do not add an anti-shock granule once the liquid is boiling.
* Place a tripod and gauze on a heat-resistant mat.
* Place the Bunsen burner underneath and connect it to the gas.
* Place the laboratory beaker of water on the gauze.
* Turn on the Bunsen lighter and open the air hole.
• Once the liquid starts to boil, close the air hole halfway and turn on the gas.
• In the end, it is always better to let the appliance cool down naturally, but
This can take a long time. If the time is short, use one of the described procedures.
* The tripod will be very hot. Take care.
• To remove very hot glasses of liquid from a tripod, the teacher must wear thermal protection gloves and surround the
Laboratory by moving the glasses for each group of students.
• If this is not possible, it is better to leave the beakers where they are until they cool down.
Turn off the gas.
* Place a commercial 'J-cloth' loosely around the hot beaker.
* Carefully tighten the fabric.
* Lift the beaker onto the heat-resistant mat.
⏳ Test tube clamps
Laboratory tongs are large tongs for gripping and lifting containers made of heat-resistant material used in high-temperature chemical reactions. Tweezers of different shapes are designed for picking up laboratory items, such as hot evaporation dishes, beakers, crucibles and other laboratory appliances.
The main type of laboratory tweezers are crucible tweezers, laboratory beaker tweezers and general-purpose ones. Most laboratory tweezers are made of: stainless steel, steel and combined steel materials, such as nickel-plated or cadmium steel. Laboratory tweezers can come with or without a protective case made of plastic.
A test tube holder is used to hold test tubes. It is used to hold a test tube in place when the tube is hot or should not be touched. For example, a test tube holder can be used to hold a test tube while it is being heated.
In addition, when heating the tube with liquid or solid contained inside, the tube holder must firmly hold a test tube so that the tube can be safely held while heating.
In particular, for heating liquids, when holding a test tube holder with a test tube, hold it so that it aligns with the laboratory bench, and also point the open end of the tube away from you or someone nearby.
In addition, while using a test tube holder, the proper distance between the test tube holder and the top of the test tube is about 3 centimeters.
Laboratory beaker price
Prices for a beaker ranges from 90 to 100%. You can also check on Amazon and place your order.
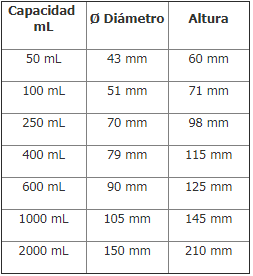
Laboratory Beaker measurements