What is method development in hplc?
Methods development in hplc and validation play important roles in the discovery, development and Manufacture of pharmaceuticals. Method development is the process of proving that an analytical method is acceptable for use to measure the concentration of an API in a specific compounded dosage form which allow simplified procedures to be employed to verify that an analysis procedure, accurately and consistently will deliver a reliable measurement of an active ingredient in a compounded preparation. The analytical method validation is essential for analytical method development and tested extensively for specificity, linearity, accuracy, precision, range, detection limit, quantization limit, and robustness. In summary, analytical method development and validation allows to confirm that an accurate and reliable potency measurement of a pharmaceutical preparation can be performed.
INTRODUCTION
The number of drugs introduced into the market is increasing every year. These drugs may be either new entities or partial structural modification of the existing one. Very often there is a time lag from the date of introduction of a drug into the market to the date of its inclusion in pharmacopoeias. This happens because of the possible uncertainties in the continuous and wider usage of these drugs, reports of new toxicities (resulting in their withdrawal from the market), development of patient resistance and introduction of better drugs by competitors. Under these conditions, standards and analytical procedures for these drugs may not be available in the pharmacopoeias. It becomes necessary, therefore to develop newer analytical methods for such drugs.
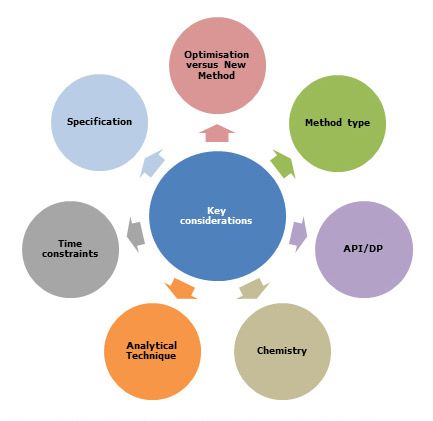
ANALYTICAL METHOD DEVELOPMENT
Analytical chemistry deals with methods for identification, separation, and quantification of the chemical components of natural and artificial materials. The choice of analytical methodology is based on many considerations, such as: chemical properties of the analyte and its concentration sample matrix, the speed and cost of the analysis, type of measurements i.e., quantitative or qualitative and the number of samples. A qualitative method yields information of the chemical identity of the species in the sample. A quantitative method provides numerical information regarding the relative amounts of one or more of the analytes in the sample.
What is method development in hplc
The steps of method development and method validation
- Method development plan definition
- Background information gathering
- Laboratory method development, it includes various stages namely sample preparation, specific analytical method, detection and data processing
- Generation of test procedure
- A well-developed method should be easy to validate. A method should be developed with the goal to rapidly test preclinical samples, formulation prototypes, and commercial samples. There are five common types of analytical methods, each with its own set of validation requirements
- Identification tests
- Potency assays
- Quantitative tests for impurities
- Limit test for the control of impurities
- Specific tests
The first four tests are universal tests, but the specific tests such as particle-size analysis and X ray diffraction are used to control specific properties of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or the drug product.
The most widely used methods for quantitative determination of drugs and metabolites in biological matrices such as blood, serum, plasma, or urine includes
- Gas chromatography ,(GC)
- High-performance liquid chromatography, (HPLC)
- Thin layer chromatography, (TLC)
- combined GC and LC mass spectrometric (MS) procedures such as LC-MS LC-MS-MS, GC-MS, and GC-MSMS, techniques like NMR is used for structure identification.


Chromatography in different forms is the leading analytical method for separation of components in a mixture. The chromatographic procedure for the separation of substances is based on differences in rates of migration through the column arising from different partition of the compounds between a stationary phase (column packing) and a mobile phase transported through the system. Chromatographic methods can be classified according to the physical state of the mobile phase into the following basic categories: gas chromatography ,(GC) supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) and liquid chromatography (LC). The technique was originally developed by the Russian botanist M.S. Tswett in 1903.
What is method development in hplc
Today TLC is rapidly becoming a routine analytical technique due to its advantages of low operating costs, high sample throughput and the need for minimum sample preparation. The major advantage of TLC is that several samples can be run simultaneously using a small quantity of mobile phase unlike HPLC thus reducing the analysis time and cost per analysis .An enhanced form of thin layer chromatography (TLC) is called as High performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC). A number of enhancements can be made to the basic method of thin layer chromatography to automate the different steps, to increase the resolution achieved and to allow more accurate quantitative measurements.
Liquid chromatography can be categorized on the basis of the mechanism of interaction of the solute with the stationary phase as: adsorption chromatography ,(liquid-solid chromatography) partition chromatography, (liquid-liquid chromatography) ion-exchange chromatography ,(IEC) size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and affinity chromatography.
Early work in liquid chromatography was based on highly polar stationary phases, and nonpolar solvents served as mobile phases, this type of chromatography is now referred to normal-phase liquid chromatography (NPLC).Chromatography on bare silica is an example of normal-phase chromatography. In reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography ,(RP-HPLC) the stationary phase is nonpolar, often a hydrocarbon, and the mobile phase is relatively polar. In RP-HPLC, the most polar component is eluted first, because it is relatively most soluble in the mobile phase.
What is method development in hplc
The definite break-through for liquid chromatography of low molecular weight compounds was the introduction of chemically modified small diameter particles (3 to 10μm) e.g., octadecyl groups bound to silica in the late 1960s. The new technique became rapidly a powerful separation technique and is today called high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
HPLC-UV diode-array detection (DAD) and HPLC-MS techniques take advantage ofchromatography as a separation method and DAD or MS as identification and quantification methods. The HPLC equipment consists of a high-pressure solvent delivery system, a sample auto injector, a separation column, a detector (UV or DAD) a computer to control the system and display results.
Ultra performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) is a recent technique in liquid chromatography, which enables significant reductions in separation time, solvent consumption and analysis time as compared to the conventional HPLC.


Sample preparation
The purpose of sample preparation is to create a processed sample that leads to better analytical results compared with the initial sample. The prepared sample should be an aliquot relatively free of interferences that is compatible with the HPLC method and that will not damage the column. The main sample preparation techniques are liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) and solid-phase extraction (SPE). In these methods the analyte of interest was separated from sample matrix, so that as few potentially interfering species as possible are carried through to the analytical separation stage.
What is method development in hplc