What is an atom in chemistry? It takes us back to the origins of the history of chemistry, it was born from the curiosity of man to understand his environment. The postulates related to the atom are realized. The same as time has passed has become specialized.
👉 What does atoms mean in chemistry?
It means that it is a very small unit of matter that possesses properties of an element. They are tiny as they measure approximately 100 Pm. The word atom comes from the Latin atomus, which means that it cannot be cut, it is indivisible and invisible. The number of protons characterizes the element to which the atom belongs.
It can bind with other atoms to form compounds. They can only be observed with a microscope. It consists of sub-atomic particles (neutrons, electrons, protons). The product of the division of an element is obtained the small particles called atoms and does not lose its chemical property.

An atom also means that
Structures are how matter is organized in nature. It is the smallest part in which matter is constituted. It is the basic unit of chemistry, since it is neither created nor destroyed. It is organized into different molecules and into another type of material. It is an identity molecule for the element.
All atoms have an equal number of protons and a variable number of neutrons, called isotopes. Not all of them have the same amount of particles in their nucleus. The diameter of an atom is 10 (-8) cm, it is the fundamental pillar of chemistry and physics.
👉Composition of the atom
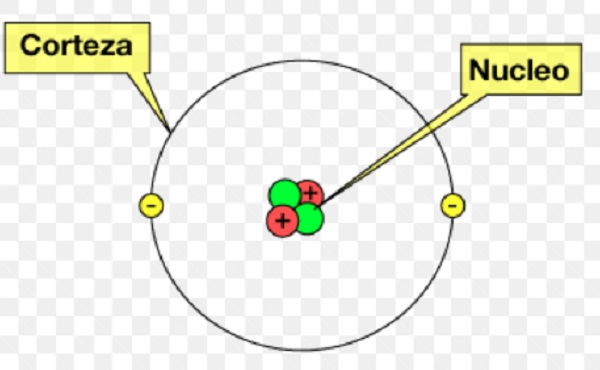
What is an atom in chemistry? it is related to how it is constituted by the outer part (cortex) and by the inner part (nucleus). The nucleus, is the center of the atom, is made up of sub-atomic particles called protons, with an electric charge (+), with an approximate weight 1.836 more than the electron. The neutron, has a weight almost identical to the proton, with a neutral charge, are known as nucleons.
It contains 99.94% of the mass of the atom. The nucleus has the charge of protons, its mass is concentrated. In the crust are located the sub-atomic particle called electrons. Those who have an electric charge (-), around the nucleus. The atom acquires a neutrality because it has the nucleus with a positive charge and in the crust electrons with a negative charge.
👉Characteristics of the atom
The characteristics of the atom are related to the chemical properties since it can be grouped to form molecules or compounds without losing them. Taking into account its constitution, it is possible to observe the differences in the different elements of the periodic table. Where the atomic number is located, which is represented as effective "Z".
It is he who points out the subatomic particles that make up its inner layer. All atoms with the same number of protons belong to an element with the same chemical properties. While the mass number is denoted by the letter "A" and is the sum of protons plus neutrons in an element.
It is known some with two equal particles of protons and also with different amount of neutrons in its inner shell. It has the chemical properties intact but the physical ones are not. This is the reason that the periodic table has been organized by the atomic numbers
👉Types and classification of atoms
The number of protons possessed by an atom characterizes the type(s) of atoms. For example, a proton in the nucleus is called a hydrogen atom, while 20 protons are equivalent to 20 calcium atoms. So yes there are different types of atoms as different numbers of protons exist in the nucleus of each element.
As many as the number of chemical elements that the periodic table has (118). The classification is based on synthetic atoms as natural. The natural ones are the ones that are found naturally in matter. 98 chemical elements have been discovered in nature. Of which 88 in natural or elemental form in appreciable quantities.
There are 10 in smaller proportion (technetium, promethium, astatine, francium, neptunium, plutonium, americium, curium, bersklium, californium).Synthetic or artificial, they are not found naturally on the planet. The artificial atoms are from Z= 99 to Z=118. Which are usually radioactive and unstable, half-lived.

👉History of the atom
It dates back to the promulgation of atomic theories. The ancient age, where the philosopher Democritus -Leucippus -Epicurus, generated the concept of atom to explain reality without experimentation. They affirmed that “Matter was not divided indefinitely, that there must be an indivisible and indestructible unity.
By bonding with other atoms, a layer is generated that surrounds it. In the year 1773 Lavoisier Antoiner postulated his statement "Matter is not created, nor is it destroyed it is transformed". In the same way he postulated the law of conservation of matter. By 1804 Dalton John, concludes that substances are composed of spherical atoms identical for each element.
But different between the elements (first atomic model). Avogadro Amadeo in 1811, postulates the theory of temperature - pressure - volume. Saying that a gas contained the same number of atoms, particles or molecules regardless of the nature of the gas. Stating that gases are poly-atomic molecules.
👉More about the history of the atom
On the other hand, in 1904 the Nagaoka model was exposed, whose model defined a gravitational relationship. For the year 1911 Rutherford Ernest, explains the internal structure of the atom. Saying that it was composed of a nucleus with a positive part and on the outside a negative part that revolved around the nucleus.
Later in the same year Bohr Niels developed the quantum theory based on the Nagaoka model. In addition, the negatively charged electrons had definite orbitals. Somerfild, gets that in an atom, an electron can reach an extraordinary small speed. He modifies Bohr's model by saying that electrons move.
Around the nucleus in circular and elliptical orbitals. That at a given energy level there may be several divisions on the same level, where a small light is visualized
What is an atom in chemistry? It is the answer to the inquiry of history where reference is made to the study of the atom, I hope it will be useful to you.

