
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) - A Comprehensive Guide
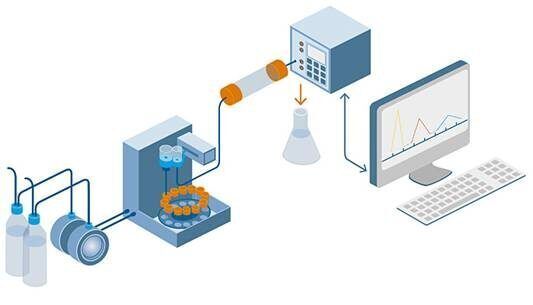
HPLC is a technique used in analytical chemistry to separate, identify, and quantify individual components in a mixture. It is a type of liquid chromatography that uses high-pressure pumps to provide high resolution and sensitivity in the analysis of complex mixtures. HPLC is widely used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food, and environmental analysis, due to its versatility and ability to provide accurate and precise results.
Principles of HPLC
HPLC is based on the principle of liquid distribution between a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The mixture to be analyzed is injected into the system, and as the mobile phase, usually a solvent, flows through the column, the components of the mixture are separated based on their physical and chemical properties. The separation is achieved by the interaction between the components of the mixture and the stationary phase, with the most strongly interacting components being retained the longest and the least interacting components being eluted first.
The stationary phase in HPLC can be a solid material packed into the column or a liquid adsorbed onto a solid support. The choice of stationary phase and mobile phase is crucial for the separation and analysis of compounds, and the method can be adjusted to optimize the separation based on the specific requirements of the analysis.
The principles of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) are based on the same underlying principles as chromatography in general. The main principles of HPLC are:
- Distribution: The components of a mixture will distribute themselves between two phases, a stationary phase and a mobile phase, based on their relative affinities for each phase.
- Adsorption: The components of the mixture will adsorb onto the surface of the stationary phase based on their molecular size and charge.
- Retention: The amount of time a component of the mixture spends on the stationary phase is called its retention time. This is determined by the component's physical and chemical properties.
- Elution: The components are separated from the stationary phase by eluting them with the mobile phase, which carries them through the column.
- Detection: The separated components can then be detected and quantified based on the method used (e.g. UV-Vis, fluorescence, mass spectrometry).
In addition to these general principles, HPLC is characterized by its high efficiency, which allows for the separation of complex mixtures with good resolution, and its versatility, which allows it to be used for a wide range of applications. These characteristics are achieved through the use of specialized instrumentation, such as high-pressure pumps and columns with small particle sizes, and by the optimization of the chromatography conditions, such as the choice of mobile phase and column temperature.
Instrumentation of an HPLC System
An HPLC system typically consists of the following components:
- Pump: The pump is responsible for delivering the mobile phase to the column at a constant and controlled flow rate.
- Column: The column is where the sample is separated based on its interaction with the stationary phase and the mobile phase.
- Injector: The injector is used to introduce the sample into the mobile phase stream and send it to the column.
- Detector: The detector is used to quantify and identify the separated components in the sample based on their specific properties.
- Data System: The data system is used to collect and process the data from the detector and display the results in the form of a chromatogram.
- Solvent Delivery System: The solvent delivery system is used to deliver the appropriate mobile phase to the pump, and to store and manage the solvents used in the analysis.
- Column Oven: The column oven is used to control the temperature of the column, which can be important for optimizing the separation of components and improving reproducibility.
These are the main components of an HPLC instrument, but there may be additional components or accessories depending on the specific application and the desired level of automation and control. It is important to select the appropriate instrumentation and accessories to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Types of HPLC
Some of the most common types of HPLC include:
- Normal Phase HPLC: In this type of HPLC, a non-polar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase are used to separate components based on their polarity.
- Reversed Phase HPLC: In this type of HPLC, a polar stationary phase and a non-polar mobile phase are used to separate components based on their polarity.
- Ion Exchange HPLC: In this type of HPLC, ion exchange resins are used as the stationary phase to separate components based on their charge.
- Size Exclusion HPLC: In this type of HPLC, a stationary phase with pores of a specific size is used to separate components based on their size.
- Hydrophilic Interaction HPLC: In this type of HPLC, a polar stationary phase and a polar mobile phase are used to separate components based on their hydrophilic properties.
- Affinity HPLC: In this type of HPLC, a stationary phase with a specific binding property is used to separate components based on their affinity for the stationary phase.
These are some of the most commonly used types of HPLC, but there are many others as well, and the choice of method will depend on the nature of the components being separated, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application.
Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is a critical step in HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) and involves preparing the sample for analysis in a way that allows for accurate and reproducible results. Some of the key steps involved in sample preparation for HPLC include:
- Sample Collection: The first step is to collect the sample, either by extracting it from a solid or liquid matrix or by measuring it directly.
- Sample Homogenization: The sample should be homogenized to ensure that it is evenly mixed and representative of the entire batch.
- Sample Purification: The sample may need to be purified to remove any interfering substances that could affect the chromatography results. This may involve filtering, centrifugation, or other purification methods.
- Sample Dilution: The sample may need to be diluted to bring the concentration of the components within the linear range of the detection method.
- Sample Injection: The prepared sample is then injected into the HPLC system, either manually or using an automatic injector.
- Sample Volume: The volume of the sample injected should be optimized to ensure that the components are well separated and that the detector is not overloaded.
These are some of the key steps involved in sample preparation for HPLC, but the specific procedures will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to follow good laboratory practices and to validate the sample preparation procedure to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Column selection and conditioning
Column selection and conditioning are important steps in HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) that can significantly impact the performance of the chromatography and the quality of the results. Some of the key factors to consider when selecting and conditioning a column for HPLC include:
- Column Type: The type of column used will depend on the nature of the sample and the desired separation mechanism. Common types of columns include normal phase, reversed phase, ion exchange, size exclusion, hydrophilic interaction, and affinity columns.
- Column Length: The length of the column will affect the resolution of the chromatography, with longer columns typically providing better resolution but slower analysis times.
- Column Diameter: The diameter of the column will affect the efficiency of the chromatography, with smaller diameters providing higher efficiency but also slower analysis times.
- Particle Size: The particle size of the stationary phase will affect the efficiency of the chromatography, with smaller particle sizes providing higher efficiency but also increased backpressure and slower analysis times.
- Pore Size: The pore size of the stationary phase will affect the separation of components based on size, with larger pores allowing for the separation of larger components but also reduced efficiency.
- Column Conditioning: The column should be conditioned before use by equilibrating it with the mobile phase and flushing it with a solvent that is compatible with the stationary phase to remove any contaminants.
These are some of the key factors to consider when selecting and conditioning a column for HPLC, but the specific procedures will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and to validate the column to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Mobile phase selection
The mobile phase in HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) is a critical component that plays a major role in the separation of components in the sample. Some of the key factors to consider when selecting the mobile phase for HPLC include:
- Composition: The composition of the mobile phase will depend on the nature of the sample and the desired separation mechanism. Common components of the mobile phase include water, organic solvents, and buffer solutions.
- Polarity: The polarity of the mobile phase will affect the separation of components based on their polarity, with polar mobile phases typically used for normal phase HPLC and non-polar mobile phases typically used for reversed phase HPLC.
- pH: The pH of the mobile phase will affect the separation of components based on their charge, with acidic or basic mobile phases typically used for ion exchange HPLC.
- Solvent Strength: The strength of the solvent in the mobile phase will affect the separation of components based on their solubility, with stronger solvents typically used for normal phase HPLC and weaker solvents typically used for reversed phase HPLC.
- Compatibility: The mobile phase should be compatible with the sample and the stationary phase, and should not interact with the components being separated in a way that could affect the results.
- Gradient: A gradient mobile phase may be used to optimize the separation of components by gradually changing the composition of the mobile phase over the course of the chromatography.
These are some of the key factors to consider when selecting the mobile phase for HPLC, but the specific composition and conditions will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to validate the mobile phase to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Detection methods
Detection is an important part of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) that allows the separated components in a sample to be quantified and identified. Some of the common detection methods used in HPLC include:
- UV-Visible Spectroscopy: This method detects the absorption of ultraviolet (UV) or visible light by the separated components, and is commonly used for non-fluorescent compounds.
- Fluorescence Spectroscopy: This method detects the fluorescence of the separated components after they have been excited by a specific wavelength of light, and is commonly used for fluorescent compounds.
- Refractive Index Detection: This method detects changes in the refractive index of the mobile phase as it passes through the detector, and is commonly used for non-absorbing or weakly absorbing compounds.
- Mass Spectrometry: This method detects the mass-to-charge ratio of the separated components and allows for their identification and quantification.
- Electrochemical Detection: This method detects the electrochemical properties of the separated components, such as their oxidation or reduction potentials, and is commonly used for biologically active compounds.
- Light Scattering Detection: This method detects changes in the light scattering of the mobile phase as it passes through the detector, and is commonly used for the detection of macromolecules such as proteins and polymers.
These are some of the common detection methods used in HPLC, but the specific method used will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to choose the appropriate detection method and to validate the detection system to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
Method development and validation
Method development and validation are crucial steps in HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) that ensure the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of the results. Some of the key steps in method development and validation include:
- Sample Characterization: The first step in method development is to understand the nature of the sample, including its composition, matrix, and potential interferences. This information is used to inform the choice of stationary phase, mobile phase, and detection method.
- Column Selection: The next step is to select an appropriate column that will provide the desired separation mechanism, based on the nature of the sample and the desired separation.
- Mobile Phase Selection: The mobile phase should be selected based on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the compatibility of the mobile phase with the sample and the column.
- Gradient Development: If a gradient mobile phase is desired, a gradient program should be developed that will provide the optimal separation of components in the sample.
- Detection Method Selection: The detection method should be selected based on the nature of the sample and the desired level of sensitivity and specificity.
- Method Optimization: The method should be optimized to improve the separation of components, reduce analysis time, and minimize the impact of potential interferences.
- Method Validation: Once the method has been developed and optimized, it should be validated to ensure its accuracy, precision, and reproducibility, and to meet any regulatory requirements. This typically involves conducting a series of experiments to demonstrate the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of the method, and to assess its suitability for the intended use.
These are some of the key steps in method development and validation, but the specific steps will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to carefully document the method development and validation process to ensure that the results are accurate and reproducible.
Aplication of HPLC
HPLC is a highly versatile technique and is widely used in various industries for a range of applications. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used for quality control, purity determination, and drug development. In the food industry, HPLC is used for the analysis of food additives, contaminants, and nutrients. In the environmental analysis, HPLC is used for the analysis of water and air samples. Some of the common applications of HPLC include:
- Quality control: HPLC is commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to perform quality control tests on drugs, dietary supplements, and other products to ensure that they meet the required specifications.
- Biochemistry: HPLC is used in biochemistry to analyze proteins, peptides, and other biological molecules to determine their composition, purity, and quantity.
- Environmental analysis: HPLC is used in environmental analysis to determine the presence and concentration of contaminants in water, air, and soil samples.
- Food and beverage analysis: HPLC is used in food and beverage analysis to determine the presence and concentration of preservatives, additives, and other contaminants in food and beverage samples.
- Clinical analysis: HPLC is used in clinical analysis to determine the presence and concentration of drugs and other compounds in biological samples such as blood, urine, and saliva.
- Forensics: HPLC is used in forensics to analyze crime scenes, identify drugs and other chemicals, and determine the presence of toxic compounds.
- Research: HPLC is used in research to isolate and identify specific compounds in complex mixtures, and to study their properties and interactions.
These are some of the common applications of HPLC, but the technique can be applied to a wide range of other fields and applications, depending on the specific requirements and objectives of the analysis. It is a powerful tool for analyzing complex mixtures and obtaining information about the composition, purity, and quantity of individual components in a sample.
Data analysis and interpretation
Data analysis and interpretation are critical steps in the HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) process, as they allow you to extract meaningful information from the results of an analysis. Some of the key steps in data analysis and interpretation include:
- Peak Identification: The first step in data analysis is to identify the peaks in the chromatogram and assign them to specific components in the sample. This may involve comparing the retention time and other characteristics of the peaks to reference standards or other known compounds.
- Peak Integration: Once the peaks have been identified, the next step is to integrate the peak areas or heights, which represents the amount of each component in the sample. This can be done manually or using software designed for chromatographic data analysis.
- Calculation of Concentration: The concentration of each component in the sample can be calculated from the peak area or height and the sample volume. This requires knowledge of the sample volume, the detection method used, and the response factor of the detector.
- Quality Control: Quality control is an important aspect of data analysis and interpretation, as it helps ensure that the results are accurate and reliable. This may involve analyzing known standards or quality control samples, and comparing the results to expected values.
- Error Analysis: Error analysis is an important aspect of data analysis and interpretation, as it helps identify sources of variability in the results and assess the accuracy of the method. This may involve calculating standard deviations, coefficients of variation, and other statistical parameters.
- Data Presentation: The results of an HPLC analysis should be presented in a clear, concise, and meaningful manner, using tables, graphs, and other visual aids as appropriate.
These are some of the key steps in data analysis and interpretation, but the specific steps will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to carefully document the data analysis and interpretation process to ensure that the results are accurate and reproducible.
Advantages of HPLC
Some of the key advantages of HPLC include:
- High Resolution: HPLC is capable of separating complex mixtures into their individual components with high resolution, allowing you to obtain detailed information about the composition, purity, and quantity of individual components in a sample.
- Speed: HPLC is a fast method, allowing you to obtain results in a matter of minutes or hours, depending on the complexity of the sample.
- Sensitivity: HPLC is a sensitive method, allowing you to detect and quantify trace levels of compounds in a sample.
- Versatility: HPLC is a versatile method, allowing you to analyze a wide range of sample types, including liquids, gases, and solids.
- Automation: HPLC is easily automated, allowing you to perform high-throughput analyses with minimal manual intervention.
- Cost-effectiveness: HPLC is a cost-effective method, especially when compared to other chromatographic methods such as gas chromatography (GC).
- Robustness: HPLC is a robust method, allowing you to obtain reliable results even with complex and challenging samples.
- High selectivity: HPLC is capable of separating compounds with similar physical and chemical properties, making it ideal for separating isomers and other closely related compounds.
These are some of the key advantages of HPLC, but the specific benefits will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. Overall, HPLC is a powerful tool for analyzing complex mixtures and obtaining information about the composition, purity, and quantity of individual components in a sample.
Conclusion
HPLC is a powerful analytical technique that provides accurate, precise, and fast results for the separation, identification, and quantification of individual components in a mixture. Its versatility and high resolution make it a valuable tool in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food, and environmental analysis. Whether you are looking to perform routine quality control tests or to analyze complex samples, HPLC is a versatile and reliable analytical method that can help you get the results you need.
¿What kind of precautions we need to take during analysis?
- Make sure the column washed before and after analysis.
- Solvents must be filtered through a 0.5 μm nylon filter membrane and degassed.
- The sample must be particle-free, therefore filtered through a 0.2 μm nylon filter membrane.
- Buffers like phosphate buffers, acetate buffers, etc. are very harmful to the HPLC system and columns they need to be washed properly.
- Don’t overload the column.
- Use appropriate flow rates to maintain system pressure.
- Do not run HPLC systems at high backpressure.
- Always use grade solvents and water derived from reliable sources.
- Use guard columns to protect against contamination and prolong column life.
- Don’t use a mobile phase or buffers with a highly acidic or basic pH.
When performing HPLC analysis, it is important to take certain precautions to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable. Some of the key precautions to consider include:
- Sample preparation: Proper sample preparation is critical for accurate and reliable results. This may involve filtering, diluting, or otherwise preparing the sample to ensure that it is suitable for analysis.
- Column selection and conditioning: The choice of column and the method used to condition it can have a significant impact on the results of an analysis. It is important to select the appropriate column and condition it according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure that the column is in optimal condition for the analysis.
- Mobile phase selection: The choice of mobile phase is critical for the separation of the components in a sample. It is important to select the appropriate mobile phase for the separation mechanism and to prepare it according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure that it is in optimal condition for the analysis.
- Detection method: The choice of detection method is critical for the accuracy and sensitivity of the results. It is important to select the appropriate detection method for the sample and to calibrate the detector according to the manufacturer's instructions to ensure that it is in optimal condition for the analysis.
- Instrumentation: It is important to regularly maintain and calibrate the HPLC instrument to ensure that it is in optimal condition for the analysis. This may involve checking the pumps, detectors, and other components of the instrument to ensure that they are functioning properly.
- Method development and validation: It is important to develop and validate the HPLC method according to established guidelines and best practices. This may involve optimizing the conditions, verifying the accuracy and precision of the method, and comparing the results to reference standards or other known compounds.
- Data analysis and interpretation: It is important to carefully analyze and interpret the results of an HPLC analysis to ensure that the results are accurate and meaningful. This may involve integrating peaks, calculating concentrations, and performing quality control and error analysis to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable.
These are some of the key precautions to consider when performing HPLC analysis, but the specific precautions will depend on the nature of the sample, the desired separation mechanism, and the specific application. It is important to carefully follow established guidelines and best practices to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable.
Glossary of HPLC
Here is a glossary of some of the most commonly used terms in High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC):
- Absorbance: The measure of a compound's ability to absorb light.
- Column: A packed column, filled with a stationary phase, used to separate components in a sample.
- Chromatography: A separation technique used to separate and analyze complex mixtures of compounds.
- Detector: A device used to measure the presence and quantity of a specific compound in the sample.
- Mobile phase: The liquid that carries the sample through the column, allowing the components to separate based on their physical and chemical properties.
- Retention time: The amount of time it takes for a specific compound to pass through the column.
- Resolution: The degree to which two peaks are separated and can be distinguished from each other.
- Stationary phase: The material packed into the column that interacts with the components in the sample, causing them to separate based on their physical and chemical properties.
- UV-visible spectrophotometer: A device used to measure the absorbance of ultraviolet (UV) or visible light by a sample.
- Van Deemter plot: A graph that plots the relationship between the separation efficiency of a column and the flow rate of the mobile phase.
- Wavelength: The distance between two peaks in a wave, used to define the color of light absorbed by a sample.
- Peak: The maximum point of a compound's signal, which indicates its presence and quantity in the sample.
The listing should be helpful to those just starting in HPLC but it also can serve as a refresher for long-time users in the field.
Brief History of Liquid Chromatography
1940s - Paper chromatography is first used to separate and analyze mixtures of compounds.
1950s - Gas chromatography (GC) is developed, using a gas as the mobile phase to separate compounds based on their volatility.
1960s - Liquid chromatography (LC) is developed, using a liquid as the mobile phase to separate compounds based on their polarity.
Late 1960s - High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) systems are developed, using high-pressure pumps to increase the flow rate of the mobile phase and improve the separation efficiency of the columns.
1970s and 1980s - HPLC continues to evolve, with advances in column technology and instrumentation making it possible to separate increasingly complex mixtures of compounds. Columns made from bonded silica and packed with smaller particles become widely available, providing higher resolution and faster analysis times. Advances in instrumentation, including the development of ultraviolet (UV) detectors, also make it possible to detect and quantify a wider range of compounds.
1990s and early 2000s - HPLC undergoes further developments, including the introduction of columns with longer lifetimes, more efficient separation mechanisms, and the widespread use of photodiode array detectors, which allow for multi-component analysis and the simultaneous detection of multiple compounds.
Today - HPLC is a highly sophisticated analytical technique that is widely used in a range of applications, including pharmaceutical analysis, environmental monitoring, food and beverage analysis, and many others.
HPLC

¿What are the Applications of Chromatography?
Chromatography is the technique for…
See more...
¿How many types of pumps are there in HPLC?
High-performance liquid chromatography is an…
See more...
¿How to avoid peak tailing in HPLC chromatography?
The broad peaks split peaks…
See more...
¿How to reduce peak broadening in HPLC?
Peak broadening Peak broadening is…
See more...
How to select a column for HPLC method development?
📋 Here you can find…
See more...Uplc vs Hplc ¿What is the Difference Between?
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
¿How to Calculate LOD and LOQ?
LOD as per the Signal-to-Noise…
See more...
¿What are the Advantages of HPLC over GC?
High-performance liquid chromatography and Gas…
See more...
¿What is the principle of HPLC?
HPLC is an analytical and…
See more...
¿What are the Applications of Paper Chromatography?
Paper chromatography is an analytical…
See more...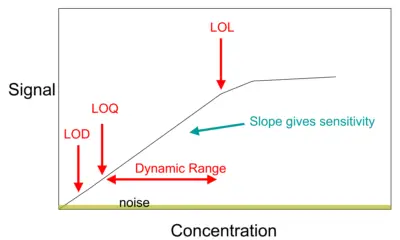
¿What is the calibration of HPLC?
The calibration of HPLC In…
See more...¿What is Hplc column? Interestings facts! Chromatography advance
Columns are the main component…
See more...
¿What are the common buffers used in HPLC?
Molecules are separated using high…
See more...
¿What is the principal of HPLC chromatography?
HPLC stands for High-Performance Liquid…
See more...
What are the Applications of Thin Layer Chromatography?
Thin Layer Chromatography It is…
See more...
¿What are the advantages of TLC over HPLC chromatography?
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is used…
See more...
Method development in hplc - Chromatography advance
What is method development in…
See more...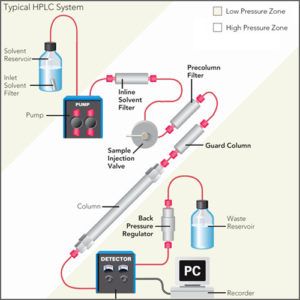
¿What is HPLC?
The first post described the…
See more...
¿Why is silica polar in HPLC columns?
The surface of silica (glass…
See more...
¿How does temperature affect paper chromatography?
Paper chromatography is a technique…
See more...
¿What is the HPLC method?
HPLC is a technique used…
See more...
¿What is preparative HPLC?
Preparative hplc involves seperating a…
See more...
¿What are the causes of broad peaks in HPLC?
Broad peaks: The presence of…
See more...
¿How to determine Loading Capacity?
Loading in chromatography refers to…
See more...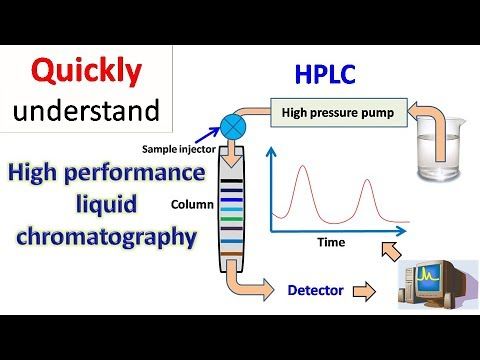
¿Which columns are used in HPLC?
This is a very general…
See more...
¿How to select a pH of mobile phase in HPLC?
When an ionizable compound in…
See more...
¿How to increase peak response in HPLC?
As we know that the…
See more...FAQ HPLC

Difference between HPLC and HPTLC
Both HPLC and HPTLC are…
See more...
Chromatography abbreviation
Some common abbreviations used in…
See more...
Adsorption Chromatography - Principle and Procedure
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
Factors affecting Rf value in TLC chromatography
During the thin layer chromatography,…
See more...
Principle and Procedure of Ion-exchange Chromatography
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
HPLC Data Analysis and Control
Today HPLC systems are controlled…
See more...Care and Maintenance of HPLC Columns
The column is packed with…
See more...
Different types of Column Chromatography
The column chromatography is a…
See more...
Applications of HPLC
HPLC is an analytical technique…
See more...
Pharmaceutical Applications of Column Chromatography
Column chromatography is a separation…
See more...
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gradient Elution in HPLC
The elution strength increases throughout…
See more...
Factors Affecting Separation in Column Chromatography
Column chromatography is most commonly…
See more...
Advantages and disadvantages of Chromatography
Advantages and disadvantages of Chromatography…
See more...
Accuracy - method validation parameter
Accuracy is a method validation…
See more...
HPLC Troubleshooting
If any problem persists during…
See more...
Applications of ion-pair chromatography
Ion pair chromatography is a…
See more...
Capacity Factor (k')
Capacity factor (k') is a…
See more...
Injection volume in HPLC
Injection volume Injecting samples into…
See more...
HPLC buffer selection guide
The high-performance liquid chromatography separates…
See more...
Advantages and disadvantages of mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is the technique…
See more...
Principle and procedure of Affinity Chromatography
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
Principle and Procedure of Paper chromatography
What is Paper Chromatography? Paper…
See more...
Selection of buffer in HPLC method development
To make an aqueous mobile…
See more...
Factors affecting column efficiency in HPLC
The column or stationary phase…
See more...
HPLC Pumps and Types of HPLC Pumps
As the name of high-pressure…
See more...
Rheodyne injector in HPLC
Rheodyne injector, septum injector, and…
See more...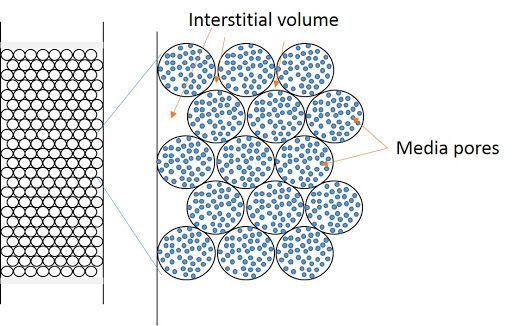
Hplc Column Volume Calculator Chromatography Advance
📋 Here you can find…
See more...Hplc Column Comparison Guide
Hplc Column Comparison Guide Search columns by…
See more...
Factors Affecting Paper Chromatography
Paper chromatography is an economical…
See more...Hichrom Hplc Column
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
HPLC Injector and Types of HPLC Injector
HPLC injection is a technique…
See more...
Factors affecting resolution in chromatography
Resolution:The resolution of elution is…
See more...
HPLC Principle and Types of HPLC Chromatography
Introduction to HPLC:HPLC is a…
See more...
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thin Layer Chromatography
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) is…
See more...
HPLC DETECTORS
The detector is the module…
See more...
Affinity Chromatography - Advantages and Disadvantages
Column chromatography is a general…
See more...
Difference between Chromatography and Spectroscopy
Chromatography:Chromatography is one of the…
See more...
Partition Chromatography / Principle and Application
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
Difference between paper and column chromatography
Chromatography is a significant biophysical…
See more...
Analytical method validation
Method validation is the process…
See more...GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY

GC Column Selection
I am often asked about…
See more...
GC Column Conditioning
If you ‘do’ Gas Chromatography,…
See more...
Special HPLC and GC columns for PAH analysis
Unmatched sensitivity and resolution for…
See more...
Ultra Inert GC Columns & Consumables
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
GC Column Degradation
Before we get on to…
See more...
GC Diagnostic | Peak Tailing
Peak tailing is a problem…
See more...
GC Diagnostic | Reduced Peak Size
We are frequently asked about…
See more...
GC Diagnostic | Baseline Problems
In Gas Chromatography (GC), perhaps…
See more...
GC Diagnostic Skills | Selectivity & Resolution Changes
This instalment in our gas…
See more...
GC Diagnostic – Loss of Efficiency (and Resolution!)
Capillary GC is renowned for…
See more...
Killer Gas Chromatography variables and other insidious ways to destroy your chromatography!
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
GC Inlet Maintenance
Many troubleshooting investigations in chromatography…
See more...
GC Carryover Problems
Let’s first properly define carry-over…
See more...
Reduction of instrument downtime
"Time is money" and an…
See more...
What makes a peak broad in gas chromatography
Sometimes troubleshooting a separation can…
See more...Advantages and disadvantages of gas-liquid chromatography
📋 Here you can find…
See more...
Difference Between Gas Chromatography and Liquid Chromatography
The main difference between gas…
See more...Advantages and disadvantages of gas chromatography
Chromatography has evolved from paper…
See more...Factors Affecting Resolution in Gas Chromatography
GC is a chromatographic separation…
See more...Gas Chromatography Furnaces
Accurately controlled column temperature in…
See more...Carrier gas by gas chromatography
Typically, nitrogen and helium are…
See more...Gas chromatography columns
In any chromatography, there is…
See more...Type of Gas Chromatography Detectors
GC detectors can find the…
See more...Principle and applications of gas chromatography
What factors influence the separation…
See more...
Principle and procedure of gas chromatography
Know the principle, types, applications…
See more...Factors Affecting Retention Time in Gas Chromatography
GC is a powerful analytical…
See more...What is Gas Chromatography?
The gas chromatography technique is…
See more...
What elutes first in gas chromatography?
As a rule of thumb,…
See more...Laboratory

Basic Bunsen Burner
Basic bunsen burner is a…
See more...
The syringe
The syringe is one of…
See more...
Instruments For Measuring Volume
Instruments for measuring volume are…
See more...
No More Doubts! Know The Types Of Chemical Reactions With Examples Included
The work carried out in…
See more...
Crucible Tweezers Should Not Be Missing In A Laboratory
The field of laboratory at…
See more...
Know The Basics Of The Bright Field Microscope And Its Uses In Research
Continuing with the line of…
See more...
Holographic Microscope And Its Comparison With The Optical Microscope
In the field of scientific…
See more...
5 Reasons To Use The Meker Burner Instead Of Another Common Burner, Find Out Here
In the laboratory there are…
See more...
The Importance Of The lab racks In The Laboratory
The work in a laboratory…
See more...
The rubber pipette bulb In The Laboratory
There are very varied materials…
See more...
Learn About The Scanning Electron Microscope And Why It Is A Favorite Of Researchers
Within the research there are…
See more...
The 5 Advantages Of The Electron Microscope Over The Conventional Optical Microscope
Since the invention of the…
See more...
Fluorescence Microscope, Get To Know Them Here
In laboratories, or rather in…
See more...
porcelain crucible In The Laboratory, Learn About Its Uses Here
Many everyday implements have been…
See more...
Everything You Need To Know About The Laminar Flow Hood In One Place
Laboratory materials, instruments, or equipment…
See more...
Discover The Seven Uses Of The Inoculation Loop In The Laboratory And Its Main Function
Laboratory instruments and materials can…
See more...
Everything You Didn't Know About Mohr Tweezers In One Place
In the laboratory every instrument…
See more...
Laboratory pipette filler And Its Special Function In The Dispensing Of Liquids
Within the laboratory materials there…
See more...
Why the Clay Triangle is the best complement to the burner
Why the clay triangle is…
See more...
FLAT BOTTOMED FLASK: What It Is For, Capacity, Use
Every good chemical professional needs…
See more...
The alcohol burner, Currently In Crisis
The alcohol burner, currently in…
See more...
The Effective Laboratory Utensil Micropipette
Laboratory micropipette, made up of…
See more...
The Differences Of Precision Balance and Analytical
The differences between the precision…
See more...
The Care Of The Analytical Balance
The care of the analytical…
See more...
What Is The Flat-bottomed Flask For?
What is the flat-bottomed flask…
See more...
What Is The Separation Funnel For?
What is the separation funnel…
See more...
The Serological And Volumetric Pipette
The differences between serological and…
See more...
What Is A Laboratory Centrifuge?
What is a laboratory centrifuge?…
See more...
The Plasma centrifuge
The centrifuge for platelet-rich plasma,…
See more...
The Bunsen Burner Chemistry Lab
The bunsen burner chemistry laboratory,…
See more...
What is a Durometer?
What is the durometer?, measure…
See more...
What is organic chemistry?
What is organic chemistry?, question…
See more...
What is microscope?
What is the microscope?, takes…
See more...
The measures of weight and mass, necessary for life
The measures of weight and…
See more...
How to distill water? A necessary procedure
How to distill water? a…
See more...
What is a chemical equation?
Chemical equations are of great…
See more...
What is a Chemical Compound?
What is chemical compound? Nowadays…
See more...
The centrifuge tube, separation essential.
The centrifuge tube is essential…
See more...
What is dilution in a solution?
What is dilution in a…
See more...
The History Of Chemistry
The history of chemistry is…
See more...
Premium Related Posts
- Cromatografia en papel
- Cromatografia en columna
- Cromatografia de columna
- Tipos de cromatografia
- Cromatografia de intercambio ionico
- Clasificación de aminoácidos
- What makes a peak broad in gas chromatography
- Clay triangle
- Water hplc
- Affinity chromatography
- Watch glass chemistry
- What is titration
- What is automatic temperature compensation
- Hplc Column Volumen Calculator
- Hplc Instrumentation
- Which drug is assay by redox titration
- HPLC Principle
- HPTLC Chromatography
- Colorimeter principle
References
A. Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org
B. Knauer: https://www.knauer.net
C. Kromasil: https://www.kromasil.com
D. Shimadzu: https://www.shimadzu.com
E. ChemistryView: https://www.chemistryviews.org
👩🔬"We hope you liked this article about High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) - A Comprehensive Guide"👩🔬
